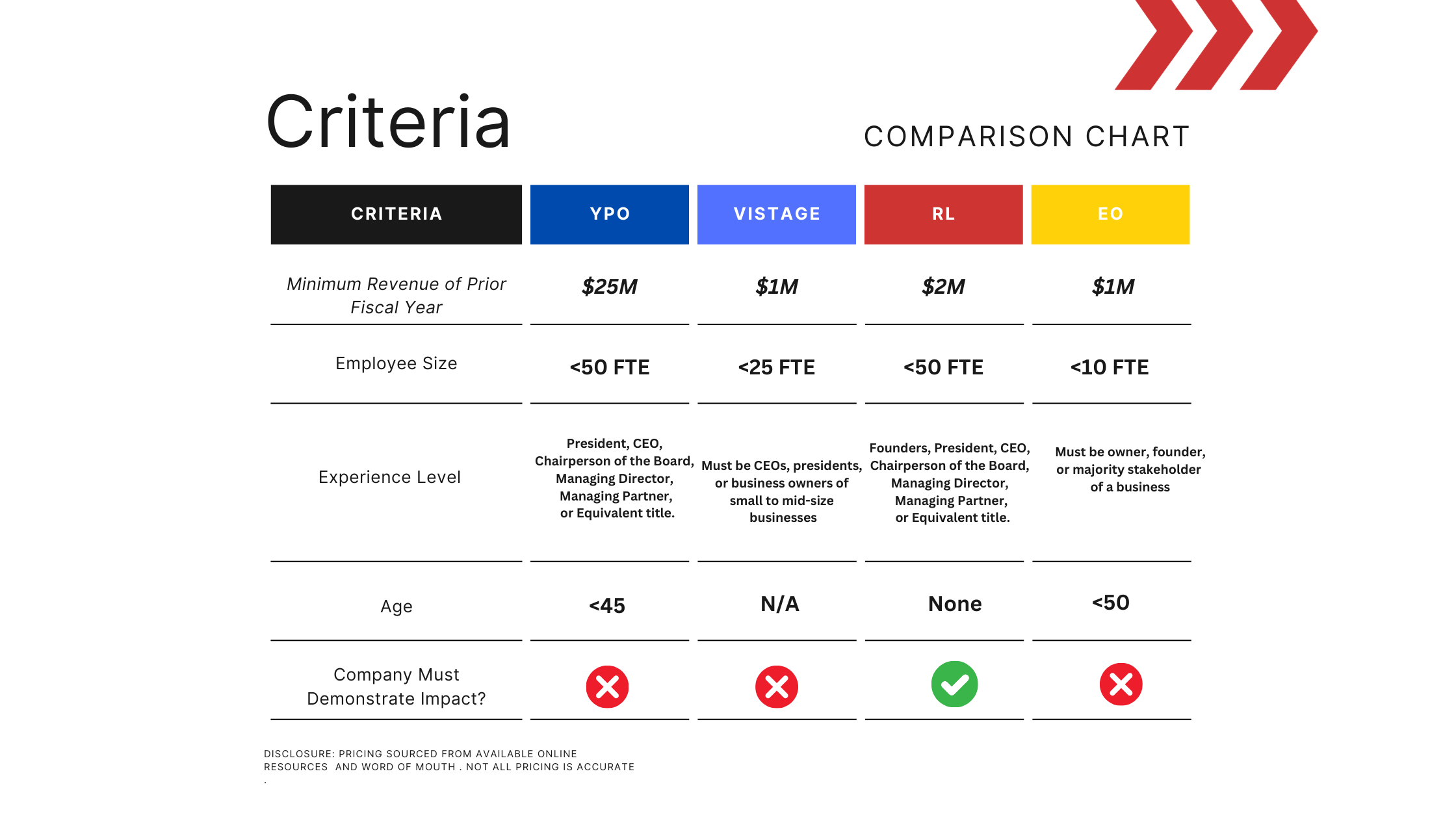
On 28 September the U.S. House of Representatives passed historic, comprehensive legislation in a vote of 393-8 that creates new resources and better policies to help the millions of patients and families impacted by substance use disorder.
Now that both Chambers have approved the final version, the package will be sent to the President’s desk to be signed into law. In an incredible show of solidarity, Congress came together in a bipartisan way to make this historic legislation a reality. Thanks to the leadership shown by politicians across the spectrum, we are one step closer to solving a crisis that affects millions of Americans and takes the lives of so many each day.
If you like this, subscribe here for more stories that Inspire The Future.
Here are 41 key components of the Opioid Package (H.R. 6):
Healthcare Integration
- Treatment, Education, and Community Help To Combat Addiction (Section 7101) – Expands medical education and training resources for healthcare providers to better address addiction, pain, and the opioid crisis;
- Preventing Overdoses While in Emergency Rooms (Section 7081) – Improves emergency departments ability to effectively screen, treat, and connect substance use disorder patients with care;
- Alternatives to Opioids in the Emergency Department (Section 7091) – Explores alternative pain management protocols in order to limit the use of opioid medications in emergency departments;
- Inclusion of opioid addiction history in patient records (Section 7051) -Requires HHS to develop best practices for prominently displaying substance use disorder treatment information in electronic health records, when requested by the patient;
Treatment Capacity Expansion
- IMD CARE Act (Section 5052) – Expands Medicaid coverage up to 30 days for individuals between 21 and 65 years old receiving care in a treatment facility for all substance use disorders, lifting the 16 bed restriction;
- Expansion of Telehealth Services (Section 1009, 2001, 3232) – Expands access to substance use disorder treatment and other services through the use of telehealth;
- Comprehensive Opioid Recovery Centers (Section 7121) – Establishes model comprehensive treatment and recovery centers to ensure individuals have access to quality treatment and recovery services;
- Supporting family-focused residential treatment (Section 8081, 8083) – Enhanced family-focused residential treatment; $20 million in funding for HHS to award to states to develop, enhance, or evaluate family-focused treatment programs to increase the number of evidence-based programs;
Treatment Workforce Expansion
- Substance Use Disorder Workforce Loan Repayment (Section 7071) – Enhances the substance use disorder treatment workforce by creating a student loan repayment program for healthcare professionals;
- Addressing economic and workforce impacts of the opioid crisis (Section 8041) – Awards grants to states to support substance use disorder and mental health treatment workforce shortages;
Medication Assisted Treatment
- More Flexibility for Prescribing Medication Assisted Treatment (Section 3201, 3202) – Increases the number of waivered health care providers that can prescribe or dispense treatment for substance use disorders, such as certified nurses and accredited physicians;
- Grants to enhance access to substance use disorder treatment (Section 3203) – authorizes grants to support the development of curriculum that will help health care practitioners obtain a waiver to prescribe MAT;
- Delivery of a Controlled Substance by a Pharmacy to be Administered by Injection or Implantation (Section 3204) – Allows pharmacies to deliver implantable or injectable medications to treat substance use disorders directly to health care providers;
- Expanding Access to Medication in In-Patient Facilities (Section 5052) – Expanded Medicaid coverage up to 30 days for inpatient facilities applies to providers who provide a minimum of two types of medicines to treat opioid use disorder;
Ending Illegal Patient Brokering
- Criminal penalties (Section 8122) – This provision makes it illegal to pay or receive kickbacks in return for referring a patient to recovery homes or clinical treatment facilities;
Recovery Supports
- CAREER Act (Section 7183) – Improves resources and wrap-around support services for individuals in recovery from a substance use disorder who are transitioning from treatment programs to independent living and the workforce;
- Ensuring Access to Quality Sober Living (Section 7031) – Develops and disseminates best practices for operating recovery housing to ensure individuals are living in a safe and supportive environment;
- Building Communities of Recovery (Section 7151, 7152) – Awards grants to recovery community organizations to provide regional training and technical assistance in order to expand peer recovery support services nationwide;
- Improving recovery and reunifying families (Section 8082) – Provides $15 million to HHS to replicate a “recovery coach” program for parents with children in foster care due to parental substance use;
Prevention
- Drug-Free Communities Reauthorization (Section 8203) – Reauthorizes the Drug-Free Communities Program to mobilize communities to prevent youth substance use and extends the National Community Anti-Drug Coalition Institute;
Helping Moms and Babies
- Sobriety Treatment and Recovery Teams (START; Section 8214) – Establishes and expands the implementation of the START program, which pairs social workers and family mentors with a small number of families, providing peer support, intensive treatment and child welfare services.
- Caring Recovery for Infants and Babies (Section 1007) – Expands Medicaid coverage for infants with neonatal abstinence syndrome who are receiving care in residential pediatric recovery centers;
- Health Insurance for Former Foster Youth (Section 1002) – Allows former foster youth to keep their Medicaid coverage across state lines until age 26;
- Modifies IMD Exclusion for Pregnant and Postpartum Women (Section 1012) – Allows for pregnant and postpartum women who are receiving care for substance use disorder in a treatment facility to receive other Medicaid-covered care, such as prenatal services;
- Report on addressing maternal and infant health in the opioid crisis (Section 7061) – Studies best practices of pain management, prevention, identification, and reduction of opioid and other substance use disorders during pregnancy;
- Early interventions for pregnant women and infants (Section 7063) – Develops and disseminates educational materials for clinicians to use with pregnant women for shared decision-making regarding pain management during pregnancy;
- Prenatal and postnatal health (Section 7064) – Authorizes data collection and analysis of neonatal abstinence syndrome and other outcomes related to prenatal substance abuse and misuse, including prenatal opioid abuse and misuse;
- Plans of safe care (Section 7065) – Supports states in collaboration and improving plans of safe care for substance-exposed infants;
Helping Patients and Families in Crisis
- Communication with families during emergencies (Section 7052) – Reminds healthcare providers annually that they are allowed under current federal privacy laws to notify families, caregivers, and health care providers of overdose emergencies involving a loved one;
- Families and Patients in Crisis (Section 8212) – Grants to expand services for patient and families impacted by substance use disorder and in crisis;
Law Enforcement
- Reauthorization of Key Law Enforcement Programs (Section 8205-8212) – Reauthorizes law enforcement programs through the Office of National Drug Control Policy, such as programs such as the High Intensity Drug Trafficking Area programs, drug courts, COPS Anti-Meth Program, and COPS anti-heroin task force program;
- First Responder Training (Section 7002) – Expands first responder training, authorized through the Comprehensive Addiction and Recovery Act, to include training on safety around fentanyl and other synthetic and dangerous substances;
- Public Health Laboratories Detecting Fentanyl and Other Synthetic Opioids (Section 7011) – Improves coordination between public health laboratories and laboratories operated by law enforcement to improve detection of fentanyl and other synthetic opioids;
- Synthetics Trafficking and Overdose Prevention (Section 8006, 8007) – Improves Federal agencies ability to detect synthetic opioids and other substances from entering the United States through the mail;
- Opioid Addiction Recovery Fraud Prevention (Sections 8021-8023) – Subjects those who engage in unfair or deceptive acts with respect to substance use disorder treatment services or substance use disorder treatment products to civil penalties for first time violations by the FTC; includes a savings clause for existing FTC and FDA authorities.
- Reauthorization of the comprehensive opioid abuse grant program (Section 8092) – Reauthorize the comprehensive opioid abuse grant program at the Department of Justice;
Prescription Medication Safety and Disposal
- Empowering Pharmacists in the Fight Against Opioid Abuse (Section 3212) – Develops and disseminates training resources to help pharmacists better detect fraudulent attempts to fill prescription medications;
- Safe Disposal of Unused Medication (Section 3222) – Allows hospice workers to dispose of unused medications on site or in patients homes;
- Access to Increased Drug Disposal (Section 3251-3260) – Awards grants to states to enhances access of prescription drug disposal programs;
- Safety-enhancing Packaging and Disposal Features (Section 3032) – Requires certain opioids to be packaged into 3 or 7 day supplies and requires safe prescription drug disposal options to be given to patients upon receiving medications;
Prisoner Reentry
- Promoting State innovations to ease transitions integration to the community for certain individuals (Section 5032) – Requires the HHS Secretary to convene a stakeholder group to produce a report of best practices for states to consider in health care related transitions for inmates of public institutions.
If you like this, subscribe here for more stories that Inspire The Future.